Submissions:Xsd:sequence embedding
From Odp
Current revision (08:31, 31 May 2010) (view source) m (Text replace - 'WOP2009:Main' to 'WOP:2009') |
|||
| (26 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Reengineering_OP_Proposal_toolbar}} | {{Reengineering_OP_Proposal_toolbar}} | ||
{{Reengineering OP Proposal General Information Template | {{Reengineering OP Proposal General Information Template | ||
| - | |Name= | + | |Name=Structural XML/DTD embedding to ontological meronymy |
| - | |Problem=This pattern addresses the re-engineering of | + | |Problem=This pattern addresses the re-engineering of certain embedded structures within XSD and DTD representations into a meronymic pattern. |
| - | + | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Reengineering OP Proposal NOR Template | {{Reengineering OP Proposal NOR Template | ||
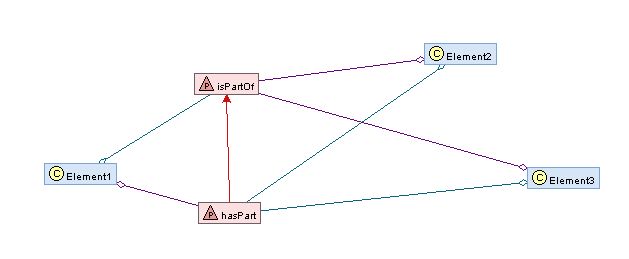
| - | |Description= | + | |Description=*For a description of XSD see: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XML_Schema_(W3C) |
| + | The pattern covers the cases where an xsd:element is embedded into an xsd:sequence, which is in its turn embedded by an xsd:element. | ||
| + | *The graphical representation only illustrates the XSD case. | ||
| + | *The DTD case is described in the example section. | ||
|Graphical Representation=1.JPG | |Graphical Representation=1.JPG | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Reengineering OP Proposal Ontology Template | {{Reengineering OP Proposal Ontology Template | ||
| - | |Description= | + | |Description=The ontology comprising the pattern representing the relevant XSD or DTD fragment. |
|Graphical Representation=Xsd-embedding2.JPG | |Graphical Representation=Xsd-embedding2.JPG | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Reengineering OP Proposal Process Template | {{Reengineering OP Proposal Process Template | ||
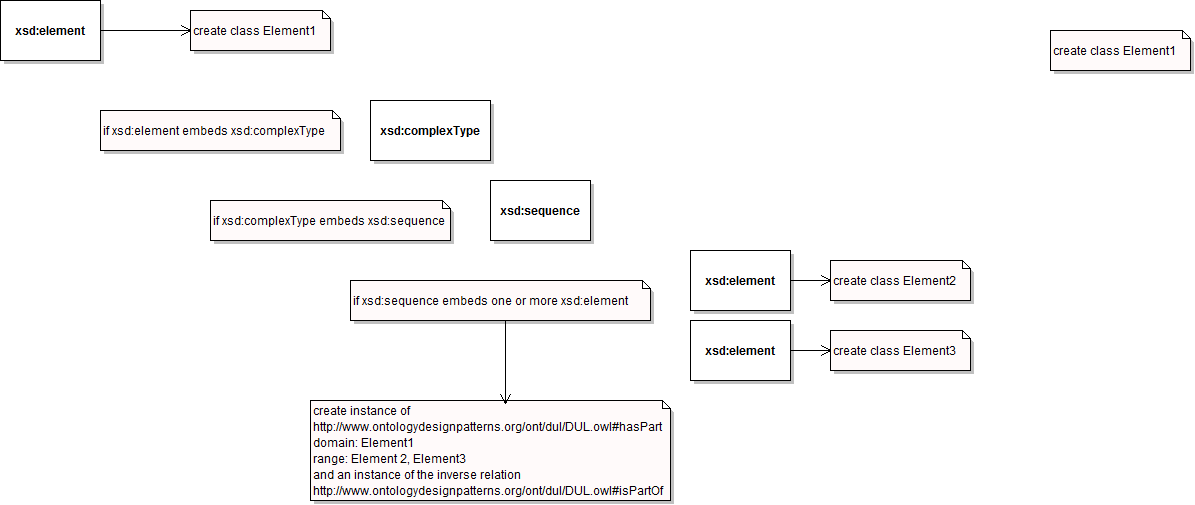
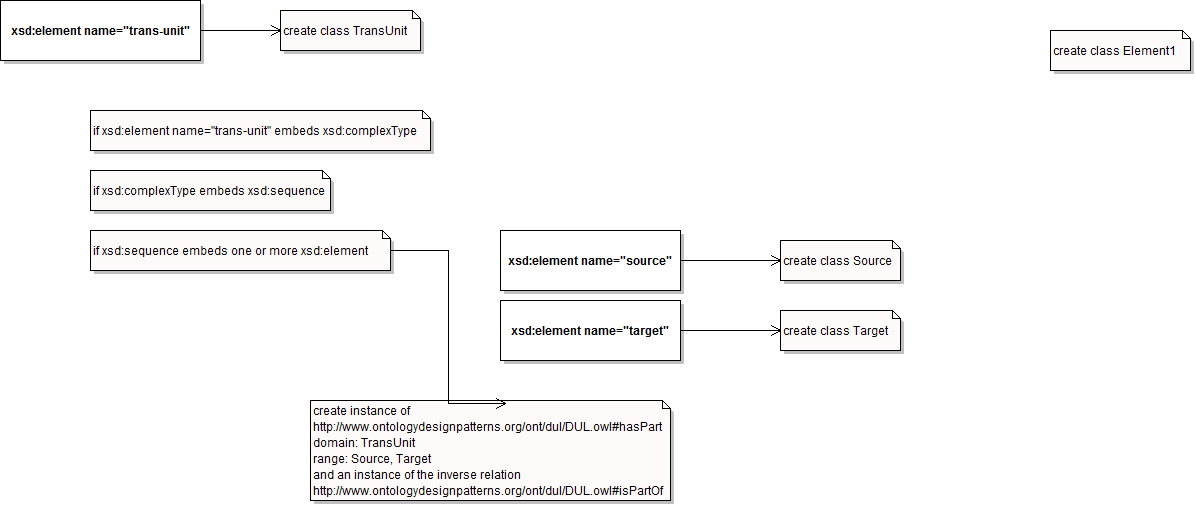
| - | |Description= | + | |Description=The re-engineering process involves a number of steps: |
| + | *The creation of embedding class and embedded class(es) | ||
| + | *The creation of an instance of the hasPart object property from the DOLCE Ultra Light ontology (http://www.ontologydesignpatterns.org/ont/dul/DUL.owl) with embedding class as domain and embedded class(es) as range. | ||
|Graphical Representation=Xsd-step3.png | |Graphical Representation=Xsd-step3.png | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Reengineering OP Proposal Scenario Example Template | {{Reengineering OP Proposal Scenario Example Template | ||
| - | |Description=The application | + | |Description=The application scenario is in the area of the modelling of lexical translational equivalence according to the format of the XLIFF and TMX standards for translation memory. |
}} | }} | ||
{{Reengineering OP Proposal NOR Example Template | {{Reengineering OP Proposal NOR Example Template | ||
| - | |Description=The purpose of the OASIS XLIFF standard (http://docs.oasis-open.org/xliff/v1.2/os/xliff-core.html) is to define and promote, through extensible XML vocabularies, the adoption of a specification for the interchange of localizable software and document based objects and related metadata. | + | |Description=XLIFF |
| + | The purpose of the OASIS XLIFF standard (http://docs.oasis-open.org/xliff/v1.2/os/xliff-core.html) is to define and promote, through extensible XML vocabularies, the adoption of a specification for the interchange of localizable software and document based objects and related metadata. | ||
XLIFF should be able to mark-up and capture localization information and interoperate with different processes and phases without loss of information. It should fulfill specific requirements of being tool-neutral. It should support the localization related aspects of internationalization and entire localization process. It also needs to support common software and content data formats. This should also provide an extensibility mechanism to allow the development of tools compatible with an implementer’s proprietary data formats and workflow requirements. | XLIFF should be able to mark-up and capture localization information and interoperate with different processes and phases without loss of information. It should fulfill specific requirements of being tool-neutral. It should support the localization related aspects of internationalization and entire localization process. It also needs to support common software and content data formats. This should also provide an extensibility mechanism to allow the development of tools compatible with an implementer’s proprietary data formats and workflow requirements. | ||
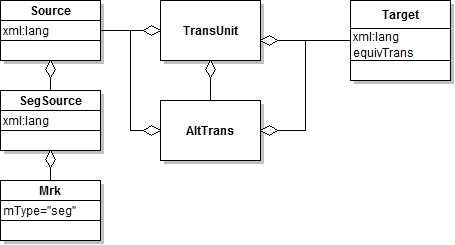
| - | 1. TransUnit: contains (a set of) translational equivalences | + | *1. TransUnit: contains (a set of) translational equivalences |
| - | 2. Source: the source of the translation pair | + | *2. Source: the source of the translation pair |
| - | 3. SegSource: the translatable text, divided into segments | + | *3. SegSource: the translatable text, divided into segments |
| - | 4. Mrk: Each segment is marked by means of the <Mrk> element with attribute | + | *4. Mrk: Each segment is marked by means of the <Mrk> element with attribute “mType” set to the value "seg". |
| - | + | *5. Target: the target of the translation pair | |
| - | 5. Target: the target of the translation pair | + | *6. Alt-Trans: possible translations as Target instances |
| - | 6. Alt-Trans: possible translations as Target instances | + | *7. Equiv-trans: Indicates if the target language translation is a direct equivalent of the source text. |
| - | 7. Equiv-trans: Indicates if the target language translation is a direct equivalent of the source text. | + | |
| + | DTD embedding is exemplified (but not illustrated on this page) by Translation Memory eXchange standard (TMX) (http://www.lisa.org/Translation-Memory-e.34.0.html). TMX is the vendor-neutral open XML standard for the exchange of Translation Memory data created by Computer Aided Translation and localization tools. The purpose of TMX is to allow easier exchange of translation memory data between tools and/or translation vendors with little or no loss of critical data during the process. In existence since 1998, TMX is a certifiable standard format. TMX is developed and maintained by OSCAR (Open Standards for Container/Content Allowing Re-use), a LISA (Localization Industry Standards Association) Special Interest Group. | ||
| + | The following structure from TMX illustrates the same pattern conversion | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!ELEMENT tu (tuv+) > | ||
| + | This describes that a translation unit (tu) consists of one or more translation unit variants (tuv). | ||
| + | A translationUnit contains the data for a given translation unit. | ||
| + | A TranslationUnitVariant specifies text in a given language. | ||
| + | A more detailed description of TMX can be found in NeOn deliverable D2.4.3: Multilingual and Localization Support for Ontologies (www.neon-project.org). | ||
|Graphical Representation=xsd-step4.png | |Graphical Representation=xsd-step4.png | ||
|Web Reference=http://schemas.liquid-technologies.com/Oasis/XLIFF/1.2/default.html?url=http://schemas.liquid-technologies.com/Oasis/XLIFF/1.2/xliff-core-1_2-strict_xsd.html | |Web Reference=http://schemas.liquid-technologies.com/Oasis/XLIFF/1.2/default.html?url=http://schemas.liquid-technologies.com/Oasis/XLIFF/1.2/xliff-core-1_2-strict_xsd.html | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Reengineering OP Proposal Ontology Example Template | {{Reengineering OP Proposal Ontology Example Template | ||
| - | |Description=The xsd:sequence embedding pattern as ontology. | + | |Description=The xsd:sequence embedding pattern as the resulting ontology pattern. |
|Graphical Representation=xsd-step5.JPG | |Graphical Representation=xsd-step5.JPG | ||
| - | |Web Reference=http://gate.ac.uk/gate-extras/neon/ontologies/xsd-embedding | + | |Web Reference=http://gate.ac.uk/gate-extras/neon/ontologies/xsd-embedding.owl |
}} | }} | ||
{{Reengineering OP Proposal Process Example Template | {{Reengineering OP Proposal Process Example Template | ||
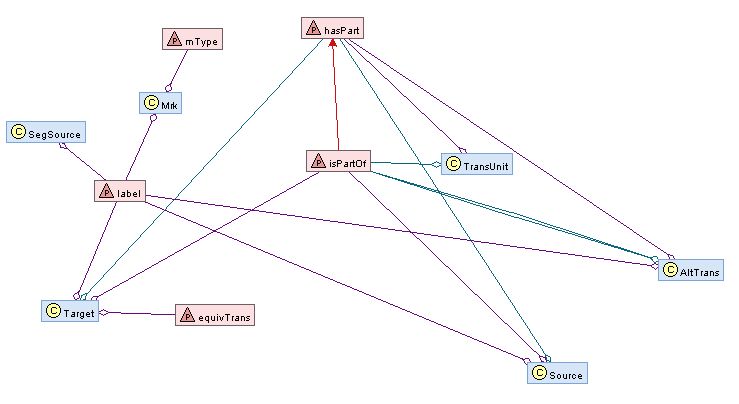
| - | |Description=The pattern | + | |Description=The ontological pattern re-engineered from the XLIFF fragment. |
| - | |Graphical Representation=Xsd-embedding- | + | |Graphical Representation=Xsd-embedding-6.png |
}} | }} | ||
{{Reengineering OP Proposal Additional Information Template | {{Reengineering OP Proposal Additional Information Template | ||
| + | |SubmittedBy=Wim Peters | ||
|Author=Wim Peters | |Author=Wim Peters | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Scenarios about me}} | {{Scenarios about me}} | ||
| - | {{Reviews about me}} | + | {{Reviews about me}}{{Modeling issues about me}} |
| + | {{Submission to event | ||
| + | |Event=WOP:2009 | ||
| + | }} | ||
Current revision

| If you are a member of quality committee please visit the
If you are author of this proposal or you want to contribute to this pattern's review, you can: ask for a review post your open review specify if this revision takes in account any of the review(s)add a new scenario for Xsd:sequence embedding In general, it could be useful to visit the evaluation section to have informations about the evaluation process of this proposal Current revision ID: 9710 |
General information
| Name | Structural XML/DTD embedding to ontological meronymy |
|---|---|
| Problem | This pattern addresses the re-engineering of certain embedded structures within XSD and DTD representations into a meronymic pattern. |
Non-Ontological Resource
| Description | *For a description of XSD see: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XML_Schema_(W3C)
The pattern covers the cases where an xsd:element is embedded into an xsd:sequence, which is in its turn embedded by an xsd:element.
|
|---|---|
| Graphical Representation |
Diagram |
Ontology
| Description | The ontology comprising the pattern representing the relevant XSD or DTD fragment. |
|---|---|
| Graphical Representation |
Diagram |
Process
| Description | The re-engineering process involves a number of steps:
|
|---|---|
| Graphical Representation |
Diagram |
Scenario example
| Description | The application scenario is in the area of the modelling of lexical translational equivalence according to the format of the XLIFF and TMX standards for translation memory. |
|---|
Example of a Non-Ontological Resource
| Description | XLIFF
The purpose of the OASIS XLIFF standard (http://docs.oasis-open.org/xliff/v1.2/os/xliff-core.html) is to define and promote, through extensible XML vocabularies, the adoption of a specification for the interchange of localizable software and document based objects and related metadata. XLIFF should be able to mark-up and capture localization information and interoperate with different processes and phases without loss of information. It should fulfill specific requirements of being tool-neutral. It should support the localization related aspects of internationalization and entire localization process. It also needs to support common software and content data formats. This should also provide an extensibility mechanism to allow the development of tools compatible with an implementer’s proprietary data formats and workflow requirements.
DTD embedding is exemplified (but not illustrated on this page) by Translation Memory eXchange standard (TMX) (http://www.lisa.org/Translation-Memory-e.34.0.html). TMX is the vendor-neutral open XML standard for the exchange of Translation Memory data created by Computer Aided Translation and localization tools. The purpose of TMX is to allow easier exchange of translation memory data between tools and/or translation vendors with little or no loss of critical data during the process. In existence since 1998, TMX is a certifiable standard format. TMX is developed and maintained by OSCAR (Open Standards for Container/Content Allowing Re-use), a LISA (Localization Industry Standards Association) Special Interest Group. The following structure from TMX illustrates the same pattern conversion <!ELEMENT tu (tuv+) > This describes that a translation unit (tu) consists of one or more translation unit variants (tuv). A translationUnit contains the data for a given translation unit. A TranslationUnitVariant specifies text in a given language. A more detailed description of TMX can be found in NeOn deliverable D2.4.3: Multilingual and Localization Support for Ontologies (www.neon-project.org). |
|---|---|
| Graphical Representation |
Diagram |
| Web Reference | http://schemas.liquid-technologies.com/Oasis/XLIFF/1.2/default.html?url=http://schemas.liquid-technologies.com/Oasis/XLIFF/1.2/xliff-core-1_2-strict_xsd.html |
Ontology example
| Description | The xsd:sequence embedding pattern as the resulting ontology pattern. |
|---|---|
| Graphical Representation |
Diagram |
| Web Reference | http://gate.ac.uk/gate-extras/neon/ontologies/xsd-embedding.owl |
Process example
| Description | The ontological pattern re-engineered from the XLIFF fragment. |
|---|---|
| Graphical Representation |
Diagram |
About
| SubmittedBy | Wim Peters |
|---|---|
| Author | Wim Peters |
| Also known as | |
| Known uses | |
| Related to | |
| Other References |
Scenarios
No scenario is added to this Content OP.
Reviews
| Review article | Posted on | About revision (current is 9710) |
|---|---|---|
| MathieuDAquin about Xsd:sequence embedding | 24550838 September 2009 | 56285,628 |
| EnricoDaga about Xsd:sequence embedding | 24550838 September 2009 | 57235,723 |
| BorisVillazón-Terrazas about Xsd:sequence embedding | 24550838 September 2009 | 57235,723 |
This revision (revision ID 9710) takes in account the reviews: none
Other info at evaluation tab
Modeling issues
There is no Modeling issue related to this proposal.
| | Submission to event |
|---|